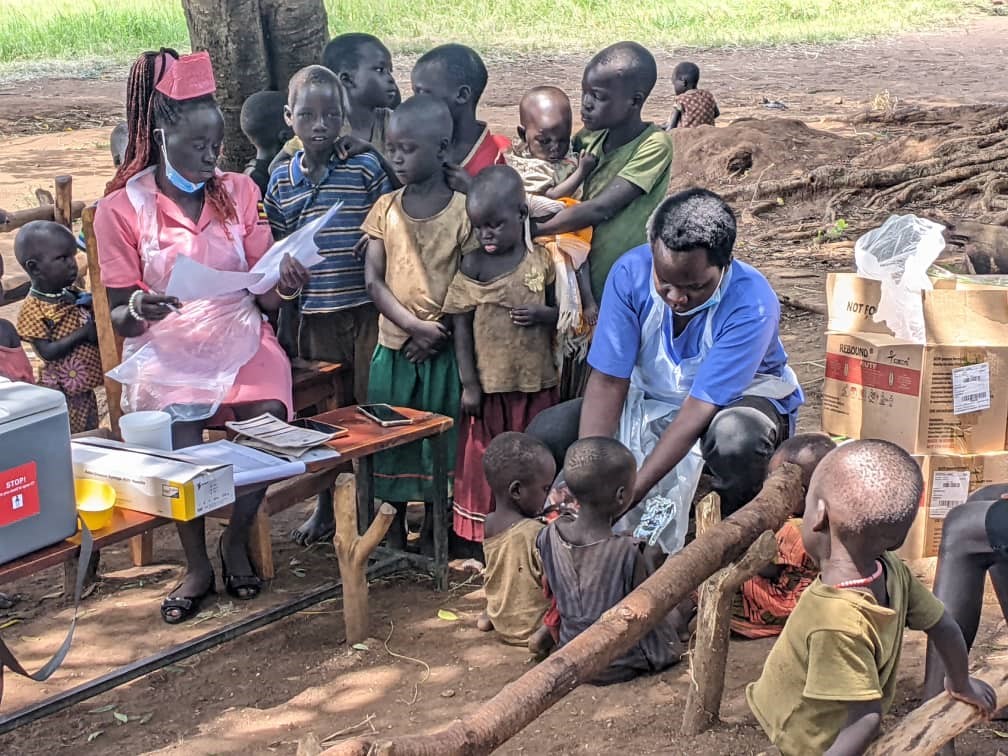
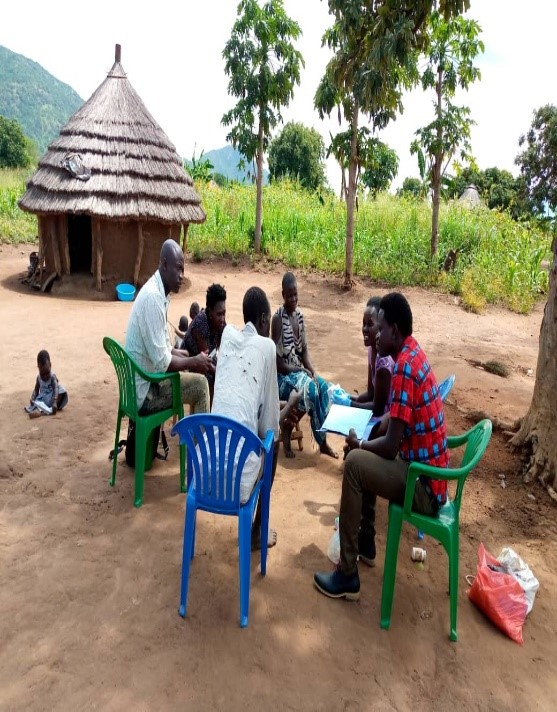
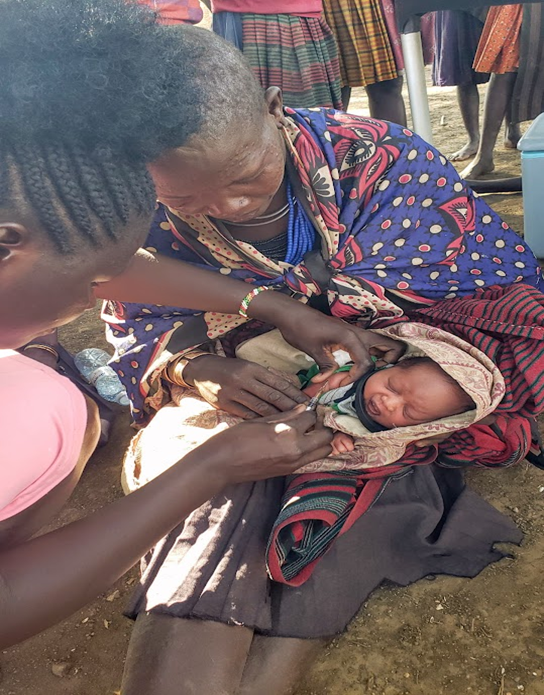
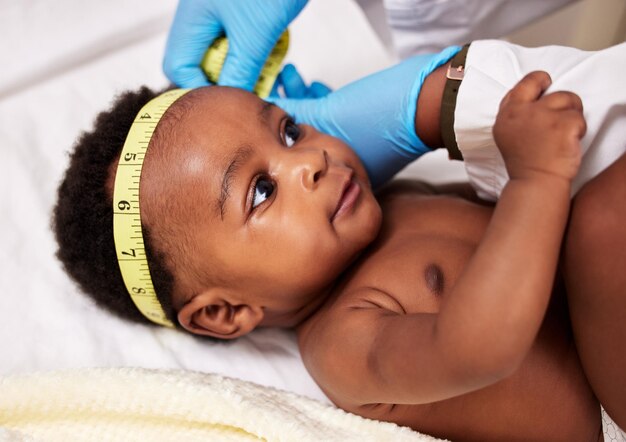
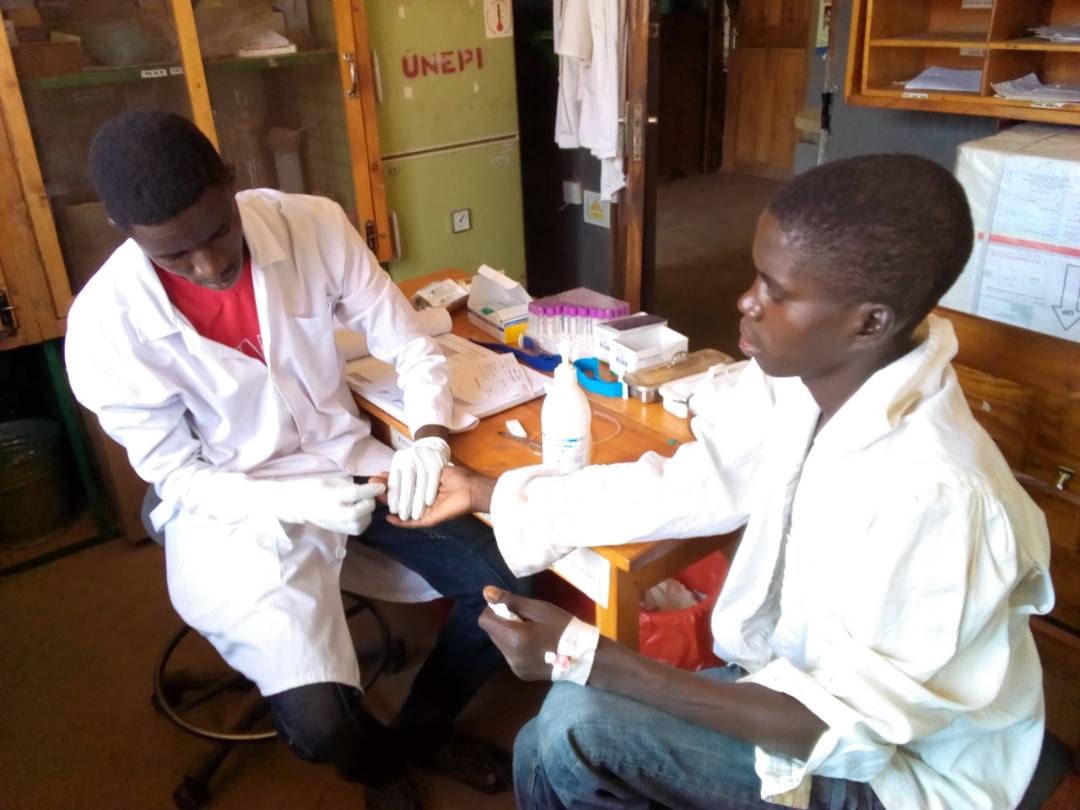
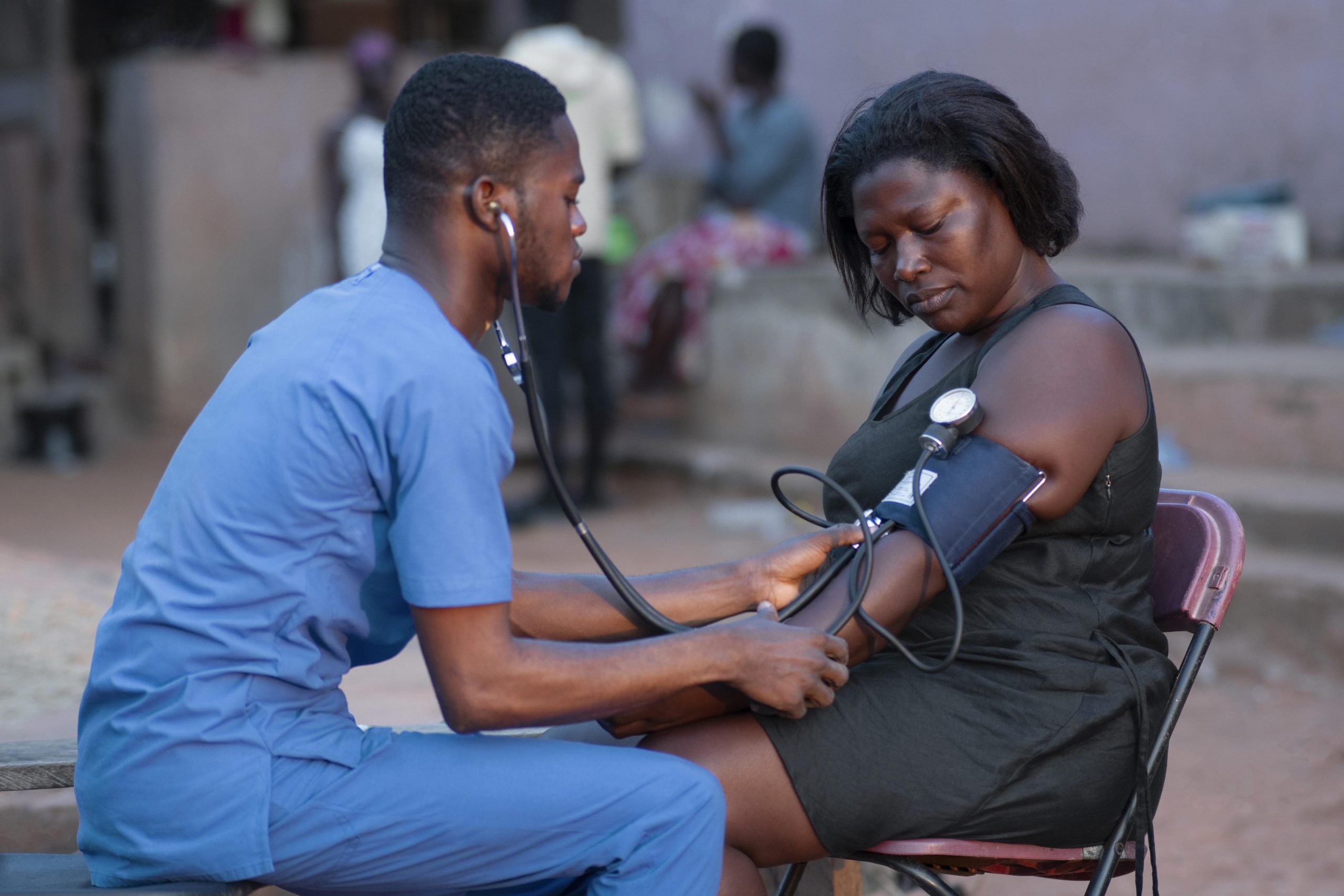Anecca is committed to improving the health and well-being of women, newborns, children and adolescents across sub-Saharan Africa. Our MNCAH program focuses on reducing preventable maternal and child deaths by strengthening health systems, enhancing service delivery, and expanding access to essential care especially in underserved and hard-to-reach communities.
We work with Ministries of Health and District Health Teams to deliver life-saving interventions aimed at reducing maternal and neonatal mortality in line with the Sustainable Development Goals.
The program approach combines evidence-based, culturally responsive and client-centred care across the continuum from pregnancy to early childhood emphasizing quality antenatal care, skilled birth attendance, postnatal follow-up, immunization, nutrition, family planning, and early childhood development.
Anecca supports a comprehensive package of high-impact interventions aligned with national strategic priorities to improve maternal, newborn, child, and adolescent health outcomes. The areas of support include: maternal, newborn, child and adolescent health.